Of the five most serious diseases in the world, flies, including mosquitoes, spread the organisms that are responsible for four: Malaria, sleeping sickness, Leishmaniasis and filariasis. They also are responsible for yellow fever, typhoid, and various diarrhea illnesses.
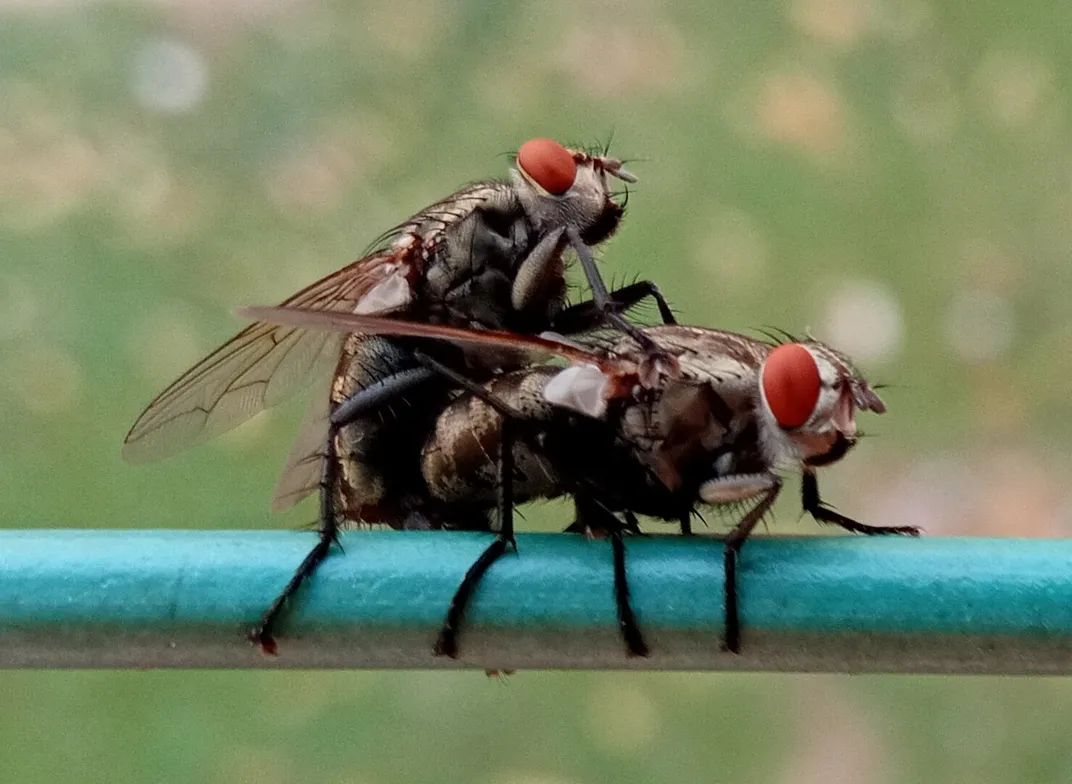

General biology and behavior
• Flies, the order Diptera, are one of the largest and most dynamic orders of insects.
• This vast order is characterized by having only one pair of wings. Most flies are also small, soft bodied; often, two large eyes that cover the front of the head.
•
Flies can be divided into two groups; distinguishing differences center around the appearance of the larvae and adults:

Prevention, treatment & proofing
Inspection
When any of these flies become problems inside, their breeding site and their larvae will usually be close by. If animals are nearby, investigate for manure concentrations.
Garbage cans and dumpsters are often the problem source; even soil where garbage has decomposed will support infestations.
• House flies infest most garbage, manure (horses, cattle, poultry, pet), filth accumulations.
• Face flies need fresh cattle manure for egg laying.
• Flesh flies, like blow flies, live in pet manure, meat scraps in garbage, and dead animals.
• Blow flies are scavengers and live in manure, carrion, dead birds and rodents in wall voids and chimneys. One Blow fly, called the Cluster fly, parasitizes earthworms.
Habitat Alteration
Caulk and tighten around all openings such as screens, doors, windows, ventilators, and eves
Remove breeding materials such as garbage and manure.
Clean garbage cans and dumpsters regularly, and any fresh overflow immediately.
Clean food delivery spills immediately and keep loading docks clean.
Drain wet areas around garbage collection sites.
Install air curtains where doors remain open for deliveries and install automatic door closer.
Replace white security lights inside and outside with yellow lights.
Pesticide Application
Fly strips can be placed in low access rooms, such as attics and storerooms
Fly bait can eliminate adult flies when methods are in place that reduce breeding sites
Electric fly traps will control only a low level of adult flies. [Watch these traps to see what kinds of flies are being caught.]
Clean food delivery spills immediately and keep loading docks clean.
Do not place black-light fly traps where they will attract insects from outside; Do not put them in competition with other lights such as those from vending machines.
Aerosol contact sprays can be used to knock down adult flies after elimination of breeding sites and exclusion methods are in effect.
Ultra-low dosage applications of non-residual pesticides can be used if an adult infestation must be quickly reduced outside.